Discover essential FX hedging strategies and currency management best practices from our foreign exchange experts.
How to Map Currency Risk
According to the recent 2021 Citi Treasury Diagnostics survey: "Corporates are now conducting comprehensive policy and ERP/TMS technology reviews with the main question being asked by senior managers: when, where and how does currency risk emerge?"
The FX risk map is a useful tool that allows us to provide answers to these fundamental questions. Toni Rami, Kantox Chief Growth Officer says: “Mapping currency risks is an essential first step in defining, selecting, and implementing risk mitigation solutions [...] If you can’t measure it, you can’t manage it”.
The FX risk map and the ‘when’ question
The FX risk map is a graphical representation of the lifespan of an FX-denominated transaction. Before a transaction is settled in cash, it is recognised in the books of the company as an invoice at the prevailing spot rate: the ‘accounting moment’ in the life of the transaction.
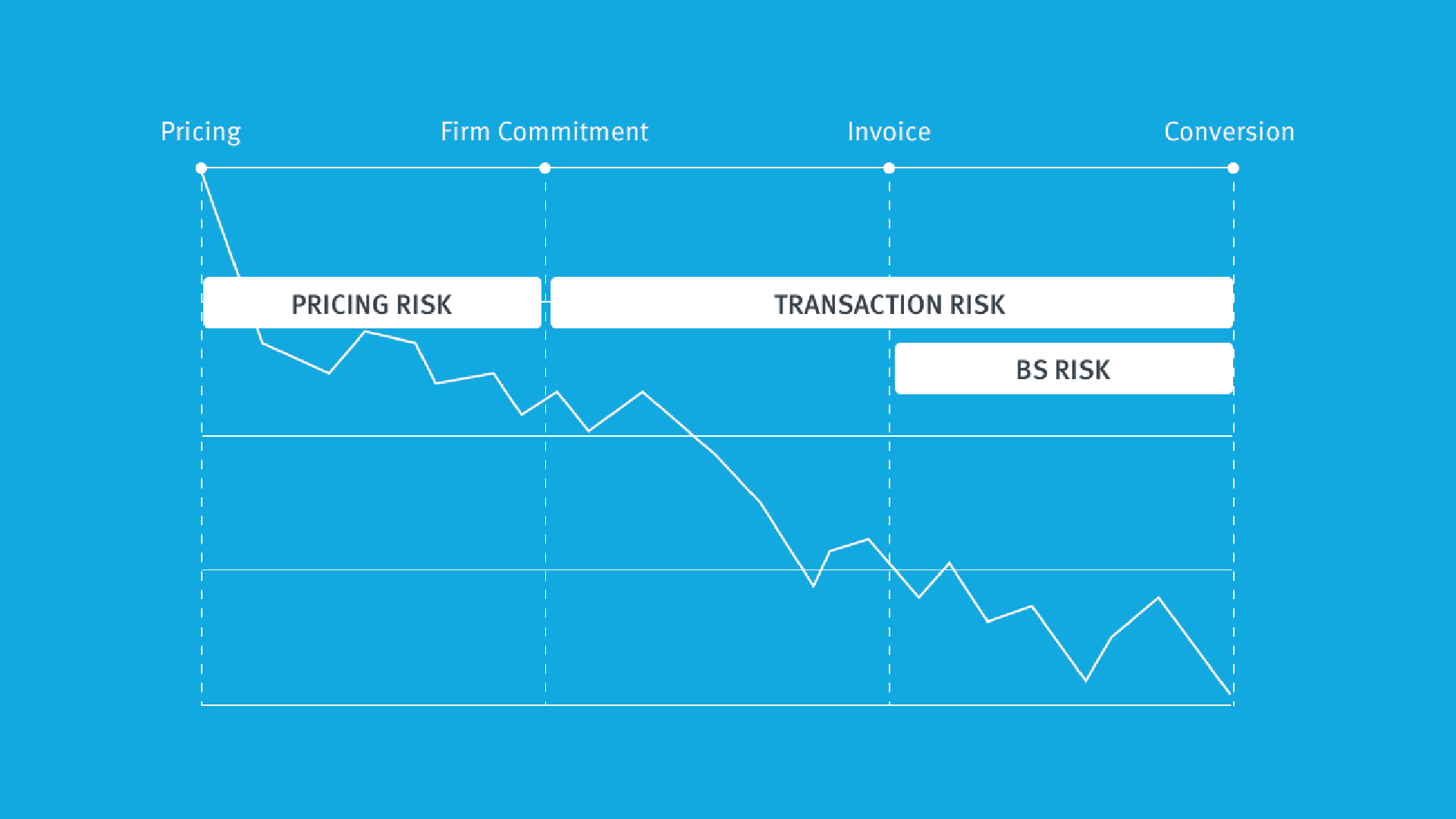
Before that, still, it is considered a firm commitment — a legally binding agreement for the exchange of a specified quantity of resources at a specified future date or dates. And even before that, it was merely a forecast, an anticipated transaction that is not yet legally binding.This, in a nutshell, describes the journey of an FX-denominated transaction. Currency risk emerges from the fluctuations in the exchange rate across the lifespan of the transaction. With that in mind, we can see that the exposure to currency risk can be classified as:
(a) accounting exposure (from the moment the invoice is recognised);
(b) cash flow exposure that includes the transaction exposure (from the firm commitments), and the forecasted exposure of revenues and expenditures.

Pricing risk
At Kantox we pay attention to another element of the FX risk map that is usually neglected in most textbooks: pricing risk. Pricing risk is the risk that —between the moment an FX-driven price is set and the moment it is updated— a shift in the exchange rate can negatively affect either your profit margins or your competitive position.
For example, if you sell in EUR and the exchange rate EUR-USD is systematically part of your pricing parameters, an appreciating USD could hurt your budgeted profit margins. On the other hand, if the EUR appreciates, your competitive position could suffer as you would be in a position to price more competitively EUR without affecting budgeted profit margins.The natural way to reduce pricing risk is to increase the frequency of exchange rate and price updates -— but that option is not available for companies that desire to keep prices steady during a single campaign or budget period, or across a set of campaign periods/budget periods linked together.
The ‘where’ question
The FX Risk Map provides answers to the questions that were raised earlier:
- When and where does currency risk arise?
- What is the proper role of your ERP and TMS when managing FX risk.
Let us see this last point in more detail:
The first thing to note is that most TMS focus on the latter part of the lifespan of a transaction, namely from the ‘accounting moment’ on to the ‘cash flow moment’. That is fine if your goal is to execute balance sheet hedging, as the exposure is made up mostly of recognised invoices.But if your goal is to execute a cash flow hedging program, most TMS fail to properly capture the relevant type of exposure: forecasts for individual campaigns or budget periods, forecasts for sets of campaigns/budget periods linked together, and firm commitments for sales and purchase orders.Moreover, they are unlikely to have the flexibility to execute combinations of hedging programs, as they must have the capacity to capture different types of exposure that sit in different systems within your company.

The solution is going to be to use currency management automation solutions, that will allow you to capture all the required information from whatever source, whatever system it is in your company, your TMS, your ERP, a booking engine and other company systems, all with the help of a single software solution.
Conclusion: towards hedging programs
The FX risk map is, of course, a simplification. Each company will have its own, more elaborated risk map than the simple version discussed today. In spite of its simplicity, the FX Risk Map allows us to better understand the when, and even the where issues of currency risk.From there, it is not difficult to see how a firm’s FX goals, combined with its pricing parameters, will result in different hedging programs: micro-hedging of firm commitments or invoices, static hedging for individual campaigns or budget periods, layered hedging for sets of campaigns/budget periods linked together, and —last but not least—, different combinations of all the above.












